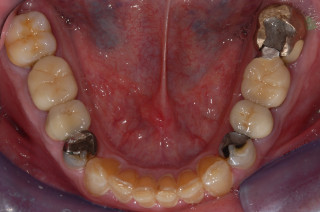
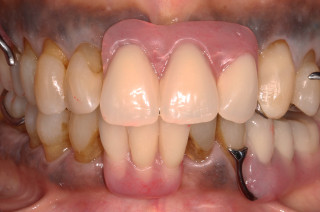
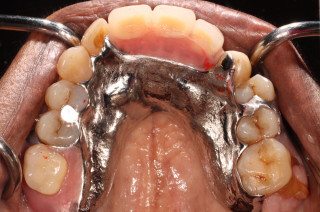
Plastic Restorations (Fillings)
Deepa works primarily with tooth-coloured fillings (composite resin). These fillings are bonded to the tooth, minimizing the need to cut down excessive tooth structure, and providing aesthetic and durable restorations.
Crowns/Onlays
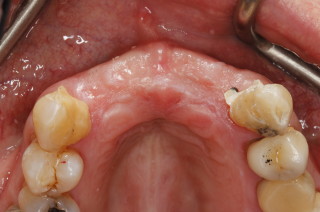
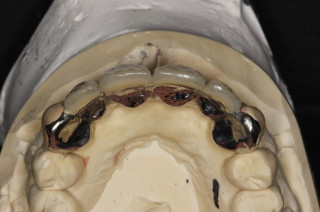
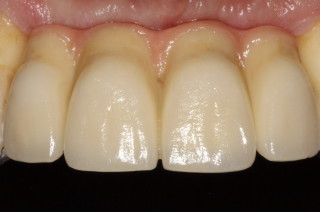
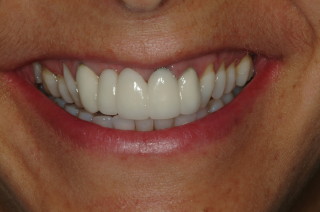
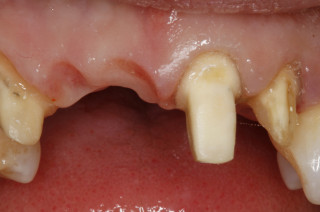
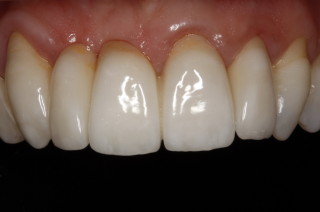
Crowns and onlays are provided to reinforce existing teeth, which may be biomechanically weakened from large fillings, cracks, or tooth wear. They will fully cover the tooth (crown) or partially cover the tooth (onlay). Several materials are available, and the choice of material that is used is based on each individual case.
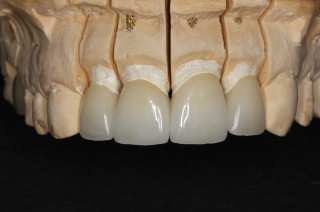
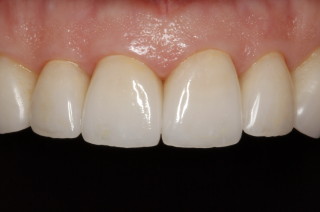
All Ceramic Crowns
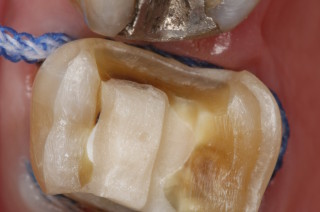
Gold Onlay
Ceramic Onlay
Bridges
Bridges are provided to replace missing teeth, using the teeth adjacent to the gap as support.There are 2 options:
Resin Retained Bridge
Conventional Bridge
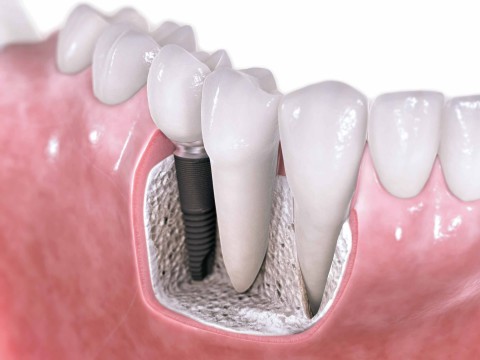
Dental Implants
Dental implants are used to replace missing teeth. The implant itself is a titanium screw that is inserted into the bone. The bone then fixes around the implant allowing a false tooth to be attached onto the implant.
There are different ways in which the false teeth are attached onto the implant, and different materials from which the teeth are fabricated. This depends on the individual case, to allow for the optimal aesthetic and functional result.
Dental implants and their restorations show very high success rates, and in the appropriate cases they are an excellent replacement option for missing teeth.
Dentures
In some cases, a fixed option to replace missing teeth may not be feasible. However, a well fitting and well-supported denture can function just as well, is very aesthetic and gives minimal complications.
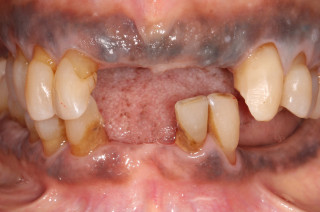
Case study
80 year old lady with missing teeth. The missing teeth were replaced with upper and lower metal-based dentures. These dentures are made to have a precision fit to the surrounding teeth, minimising movement and maximising stability. They are tolerated very well, and can give an excellent aesthetic result.
Root Canal Therapy
What is root canal therapy?
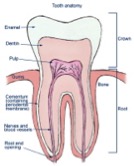 Each tooth is made up of layers of hard tissue (enamel and dentine), and these encase the dental pulp. The dental pulp contains nerves and blood vessels which help the tooth to function. However, various insults (tooth decay, cracked teeth) can penetrate the hard tissues and bacteria are allowed to enter the pulp. This means the pulp becomes infected and inflamed. The signs of an infected and inflamed pulp are pain, sensitivity to hot or cold, tooth discolouration or pain on biting.
Each tooth is made up of layers of hard tissue (enamel and dentine), and these encase the dental pulp. The dental pulp contains nerves and blood vessels which help the tooth to function. However, various insults (tooth decay, cracked teeth) can penetrate the hard tissues and bacteria are allowed to enter the pulp. This means the pulp becomes infected and inflamed. The signs of an infected and inflamed pulp are pain, sensitivity to hot or cold, tooth discolouration or pain on biting.
Once a dental pulp is affected beyond repair, the infected tissue must be removed. This will address the pain, and also serve to seal the tooth to prevent more bacterial from entering the pulp space.
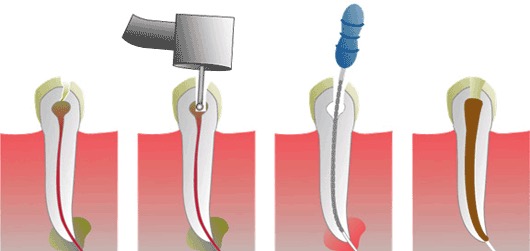
The procedure is carried out with local anaesthetic, and is relatively comfortable and rarely causes pain. It can be completed in 1 or 2 visits. After the treatment, the tooth may be slightly sensitive or uncomfortable, but this is usually managed with over-the-counter painkillers.
If your case is particularly complex, you may be referred to an Endodontist (specialist in root canal treatment).
Periodontal Therapy

Periodontal therapy is concerned with the treatment of gum disease.
Gum disease is an inflammation and infection of the gum tissues and/or the bone, which support the teeth. Bacteria are present in the mouth, and collect within the plaque or tartar on the teeth. If this plaque is not removed adequately on a daily basis it causes an inflammatory reaction of the gums, and as the disease progresses the bone is affected.
Signs and symptoms of gum disease are bleeding gums, bad breath, pain and later on the teeth can become loose.
Prevention
Gum disease can be prevented with good tooth-cleaning regimes at home, including brushing and flossing daily.
It is also important to see a dental hygienist on a regular basis for professional cleaning of inflamed sites, or areas which are difficult to maintain at home. The hygienist will also ensure that your tooth cleaning is effective, and will be able to advise on preventive regimes related to other problems such as tooth decay and erosion.
Treatment of gum disease
There are 2 forms of gum disease. Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gum tissues. Periodontitis is inflammation and infection of the gums and the bone, is more severe and can result in tooth loss.
Treatment protocols are similar, involving oral hygiene advice to improve your tooth-cleaning at home, as well as deep cleaning with the dentist or hygienist. More severe cases may require referral to a Periodontist (dentist specialising in gum disease).
Occasionally, medical conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, pregnancy and certain medications can cause an aggravated response to the plaque bacteria. This will be discussed with you, and every treatment protocol is tailored for each specific case.